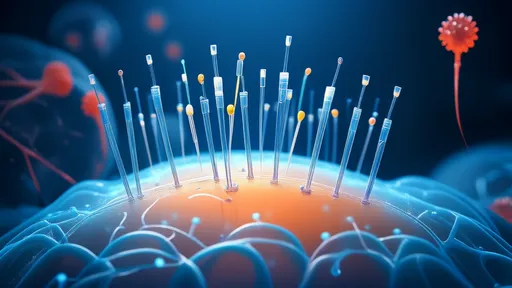
In a groundbreaking development that could redefine the future of anti-aging therapies, researchers have unveiled a novel "longevity microneedle" patch capable of delivering telomerase directly to target cells. This innovative approach combines the precision of targeted drug delivery with the convenience of a wearable patch, offering a promising solution to one of biology’s most persistent challenges: cellular aging. The implications are profound, potentially opening doors to treatments that extend healthy human lifespan while addressing age-related diseases at their root.
The science behind this breakthrough hinges on telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with each cell division. When telomeres become critically short, cells enter senescence or apoptosis—a key driver of aging. Telomerase, an enzyme that elongates telomeres, has long been considered the holy grail of longevity research. However, delivering it safely and effectively has remained an obstacle. Systemic administration risks unintended consequences like cancer cell proliferation, where telomerase is often hyperactive. This is where the dissolvable microneedle (DMN) patch changes the game.
How the Patch Works: The dime-sized device features hundreds of biodegradable microneedles loaded with telomerase mRNA or the enzyme itself. When applied to skin, these needles painlessly penetrate the outer layer, dissolving within minutes to release their payload into underlying tissues. Unlike traditional injections, the patch achieves localized delivery, minimizing systemic exposure. Early animal studies show the technology can selectively rejuvenate tissues—imagine applying a patch to sun-damaged skin to reverse photoaging or treating age-related muscle loss by targeting specific muscle groups.
What sets this approach apart is its spatial control. Researchers engineered the microneedles to release telomerase only within certain layers of tissue, creating what they call "longevity microzones." In mouse models, patches applied to thin skin areas extended telomeres in nearby cells by up to 30% within weeks, without affecting untreated areas. This precision reduces the risk of off-target effects, a critical advantage over oral or intravenous telomerase therapies. "It’s like applying a bandage that not only covers a wound but actively rewinds the aging clock in that exact location," explains Dr. Elena Voss, a biogerontologist unaffiliated with the study.
The Safety Factor: Critics have rightly questioned whether telomerase delivery might inadvertently fuel precancerous growths. The team addressed this by incorporating a dual-release system: telomerase is paired with tumor-suppressing miRNAs that act as molecular "safety switches." In human cell cultures, this combination extended telomeres while suppressing markers of malignant transformation. While long-term studies are needed, preliminary data suggest the risk profile may be more favorable than genetic telomerase activation approaches.
Beyond cosmetics and muscle repair, researchers envision therapeutic applications for conditions like chronic wounds and degenerative joint diseases. Diabetic foot ulcers, which struggle to heal due to shortened telomeres in skin cells, showed 70% faster closure rates in treated animals. Orthopedic applications could revolutionize osteoarthritis care by rejuvenating cartilage cells—a tissue notoriously difficult to target with conventional drugs. The patches might even be adapted for transdermal vaccine delivery, leveraging the same technology to boost immune cell longevity.
Commercialization hurdles remain, including scaling up production and navigating regulatory pathways for what could be classified as both a drug and device. Yet investor interest is surging, with venture capital firms specializing in longevity therapeutics backing the project. As Dr. Voss notes, "This isn’t just another anti-aging cream claiming to turn back time—it’s a measurable, targeted intervention rooted in decades of telomere research." Human trials are expected within two years, potentially marking the dawn of a new era in precision longevity medicine.
The ethical dimensions loom large as well. If proven effective in humans, such technology could exacerbate healthcare inequalities or be misused for purely cosmetic purposes. Some bioethicists argue for preemptive guidelines to ensure equitable access and prevent exploitation. Meanwhile, the scientific community watches closely—this innovation may well represent the first practical step toward controlled cellular rejuvenation, bridging the gap between laboratory discoveries and real-world applications that could extend human healthspan.

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025
By /Aug 18, 2025
By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025
By /Aug 18, 2025

By /Aug 18, 2025
By /Aug 18, 2025